“What would an academic degree look like if it were designed today? Or a professional certificate? Or a certificate for an online course? As the question of trusted verification and authentication of learning and credentials arises with increased urgency, we need to redesign the way we issue, recognize and transact with academic credentials” – Digital Credentials Consortium.
Diplomas and qualifications, security clearances, driving licenses, identity cards, passports, etc. We all own credentials like these in paper form. However, from lost documents through to theft and falsification, paper credentials can cause many inconveniences.
The challenge of free access to certified digital micro-credentials is a key issue, and is particularly relevant in the world of academia, where several leading international projects are being developed. This challenge is up against the evolution of digital practices, and the proliferation of professional social networks, short courses and programs, and micro-credentials, demanding we rethink credentials (e.g. digital diplomas, transcripts, Open Badges, micro-certs, etc.).
Beyond technical aspects, the values of block-chain ecosystems are particularly in line those of the academia, such as transparency, durability, and the free use of digital credentials by students. With the use of these new technologies, the issue of interoperability of solutions and standards is key for the efficiency of the work and experiments underway.
Digital technologies are creating new opportunities and perspectives for everyday certifications. So, let’s take a closer look at digital credentials: what are they about, how they are used, and what kind of innovation can we expect in the near future?
In this article, we discuss the major challenges of digital credentials: the role of private data, storage, scalability, and emerging standards. We detail the use case developed by BCdiploma, the first blockchain-based credentials ecosystem in production with almost a hundred universities and schools in 21+ countries.
The definition of digital credentials
Digital credentials are digital certifications issued by a given institution: diplomas, blocks of competences, transcripts, etc.
They are a digital version of these traditional documents. Just like their paper counterparts, digital credentials are issued by academic establishments, public service institutions, and so on. And just like paper credentials, digital credentials hold genuine evidential value.
Digital credentials are really no different from physical credentials, such as a passport. Just as when you present your passport at a border control, when you apply for a job or a university program, you need to be able prove you have the necessary qualifications.
In today’s fast-paced, online-first world, dominated by apps, web pages and social media, you need to be able to do this instantly, in a digital way. Rather than asking your old university for expensive paper copies, and to send them by snail mail. Or send a PDF copy that may easily be forged by other candidates.
How exactly can we define Digital Credentials?
Digital credentials are forgery-proof, fully validatable and 100% digital certificates and badges. They are the exact digital equivalent of paper diplomas. We are all familiar with paper versions of passports, driver’s licenses, diplomas, course certificates, titles of ownership, etc. Imagine a digital version of all these documents that can be verified online and cannot be falsified… and that’s a digital credential! Of course, to be recognized by everyone as documents with probative value, standardization and a lot of informative work is necessary. This work of standardization is led by the World Wide Web Consortium (W3C). As for the informative work, read this article for a start!
Here are the keywords to describe a digital credential:
- tamper-proof;
- verifiable online, without third-party querying;
- usable without time limit if not revoked;
- usable on any platform using the Verifiable Credentials standards (W3C).
Here is an example of a digital credential issued by the University of Lille:

How do digital credentials work?
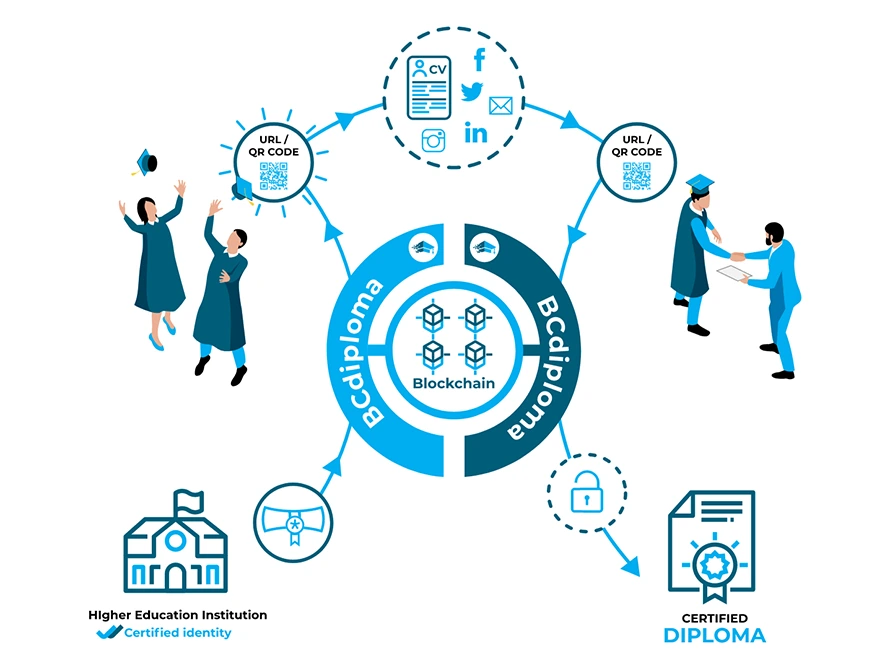
The BCdiploma (Blockchain Certified diploma) solution certifies credentials by direct storage on a block-chain, based on a framework that guarantees the authenticity and confidentiality of all the information stored.
The application, which controls access, as well as the writing and reading of the information, is a decentralized application (DApp). The BCdiploma DApp integrates all the features required by the solution and provides users (institutions, graduates, recruiters) with ease of use.
The BCdiploma DApp was developed to enable:
- Reading and writing data in the blockchain;
- Encryption and therefore protection of personal information;
- Storage of encryption keys;
- Data visualization (multilingual diplomas) fvia a simple URL link that can be shared by the graduate.
What are the three types of credentials users?
Appendix 1 – The three types of users
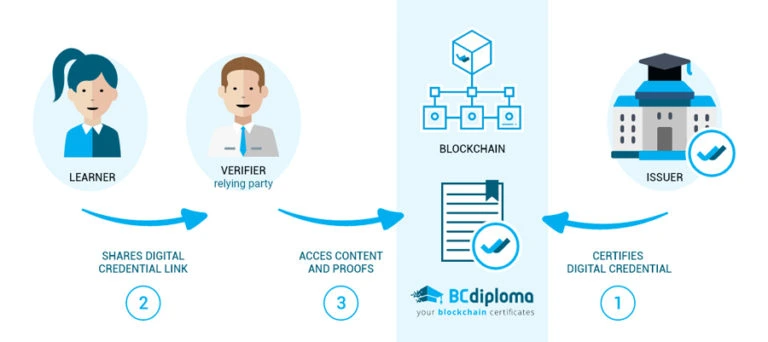
The BCdiploma solution addresses three types of users:
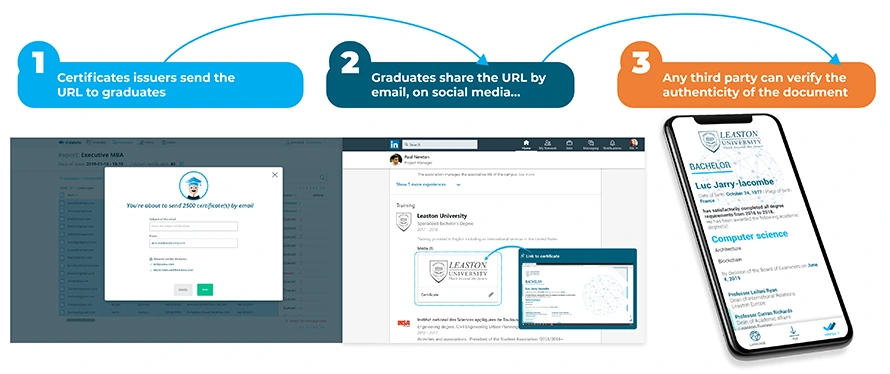
- For institutions (“issuer“): Each new institution has its identity verified upon registration by third party validators. Once its identity has been verified, the institution, a university or college for instance, has a certified address on the Ethereum block-chain and can upload its diplomas using the BCdiploma DApp (operating in the cloud) deployed as a SaaS solution. The submitted diplomas are then automatically encrypted by the solution and registered through an Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM) transaction, or Ethereum or Smart Chain, for example. The key for decryption is divided into three parts: one for the institution, one for the graduate, and a last one, called “persistence”, stored in a keystore. The storage of the diploma then generates a unique and secure URL link that the institution can securely send to the graduate concerned. Finally, the application sends a completion report to the issuer institution.
- For graduates (“learner“): each graduate is assigned a unique URL link to their diploma. The encryption key is included in the URL and allows access. The graduates is free to share this URL link at their discretion: they can choose to send it only to recruiters and potential employers, or to post it on a social network such as LinkedIn to prove the authenticity of their achievements. If they wish, graduates can use their right to be forgotten to make the diploma indecipherable by removing the associated persistence key.
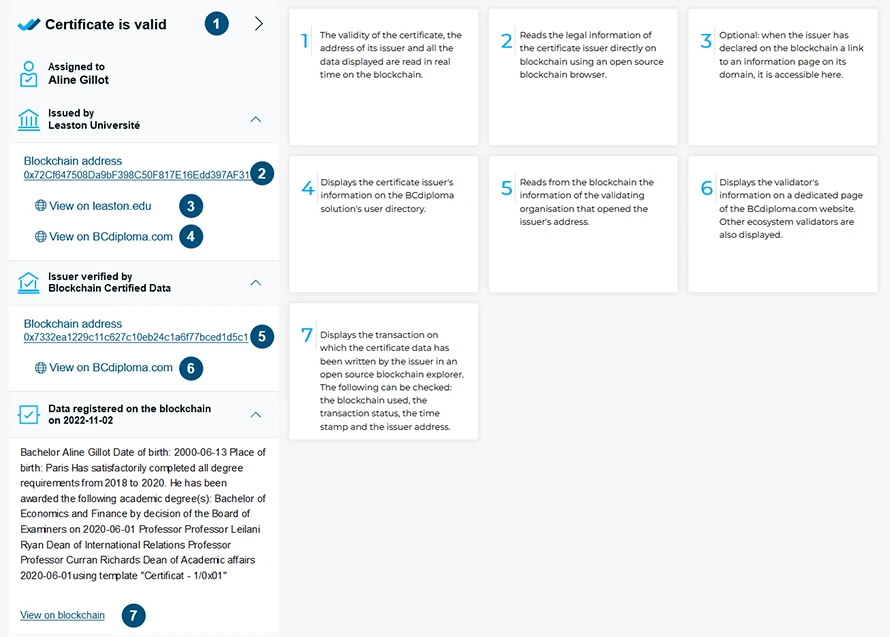
- For recruiters (or third parties consulting the credential – “verifier“): having the URL of the diploma allows recruiters or potential employers to directly verify its authenticity. The visualization of the diploma is done via the “Reader” app, a component of the DApp of BCdiploma. This makes it possible to verify the authenticity of the diploma and its validity. At each reading, a set of verifications are automatically carried out, and can be checked on the block-chain, including the validity of authorizations made by the issuer of the diploma, the non-deletion of the diploma, and the authorized information that can be displayed. All the information accessed is read in real-time, and BCdiploma is the only player managing the process.
How can we prevent digital credentials from being forged ?
One of the problems of the digital world is that digital things tend to be extremely easy to copy. Another candidate can view someone else’s degree document online, take a screenshot, change the name in Photoshop, and present it in the same application process as you.
It’s clear that the old digital technology of sharing images or document files, in formats such as JPEG, DOC or PDF, is simply no longer good enough. Although, sharing a visual image is the absolute fastest way of communicating the necessary.
So how can we bring the ease of sharing a visual file together with the need to prevent forgeries? The solution lies in the latest conception of the internet, that is Web 3.
First came Web 1.0, or the read-only web. Next came Web 2.0, that is, the interactive, collaborative or sharing web. This is the conception of the web that most of us recognize today. That of social media networks such as Facebook, LinkedIn, TikTok, Twitter, and so on.
Just now coming over the horizon is Web 3.0. This is the so-called “semantic web”, which incorporates artificial intelligence chat-bots and virtual assistants, the 3D digital recreation of the actual physical world inside computers, known as the “metaverse”, and the secure encryption of digital objects and information, using block-chain technologies.
Why is this new version of the web called “semantic”? Well, because it allows information to be not only connected (as the Web 1.0) and shareable (as the Web 2.0), but also immediately interpretable and accredible by both individuals and machines. This makes it possible to embed an image or e-badge of a digital degree in a web or social media page, and for a human or a machine to instantly check it’s the real deal, and not a forgery.
Credential user journeys
Appendix 2 – Blockchain Credential issuers user journey

Appendix 3 – Graduates and third parties’ journey
Compatibility with Open Badges, Verifiable credentials and DID standards
Interoperability between standards and ecosystems is one of the major challenges for the coming years. BCdiploma allows you to embark on the blockchain adventure with a framework that offers, by design, compatibility with open standards, whether they are already in use as Open Badges, or in the process of being implemented, such as Verifiable Credentials.
How does it work? The BCdiploma technology provides one-click access to certified and stored data, but without imposing a fixed data model. Each issuing institution is free to use its own data model.
When the data model used is compatible with the desired standard (Open Badges or Verifiable Credentials), the online blockchain certificate, called blockchain digital credentials, is recognized by the services or platforms using this standard. In other words, BCdiploma addresses the dual challenges of storage and exchange format. The Open Badges by BCdiploma product has been certified by 1EdTech – IMS Global.
Of course, the key question remains the use of decentralized DID identifiers to link the identity of the certificate holder to the credential. The development of the decentralized identity systems is ongoing, and BCdiploma interacts with these DIDs by enabling the cryptographic signature of the Digital Credential by its holder, via the DID.
BCdiploma thus received a grant from EBSI & NGI ESSIF Lab to implement this system based on the DID of the European EBSI Blockchain. In June 2022, BCdiploma publishes its work on the validity of Verifiable Credentials issued on the EBSI blockchain.

Technical aspects of the credentials solution
The public block-chain is an efficient tool for the development of certification and notarization solutions. Its intrinsic property of distributed trust ensures the immutability of recorded information. In addition, it facilitates the creation of smart contracts, real contracts that are automatically performed after all the parameters have been checked.
However, there are three key issues in the use of the blockcerts to build a solution for the general public to certify documents:
- How is the issuer identity ascertained?
- How is the GDPR complied with?
- How is it possible to view a credential immediately, i.e. without complex or centralized validation, management and processing?
By answering these three questions, the BCdiploma solution enriches the state of the art. In 2018, the company filed a patent describing its process, which was granted on its first reading and in its entirety in the US in July 2020.
Different components are deployed via EVMs, including an application part and key registries deployed in the Microsoft Azure cloud.
BCdiploma’s main smart contract is deployed on Ethereum, and its Identification, Validation and Publication methods help to answer question 1.) How is the identity of the issuer verified?help to answer the question (1.) How is the identity of the data issuer verified?
Appendix 4 – Main features of the smart contract
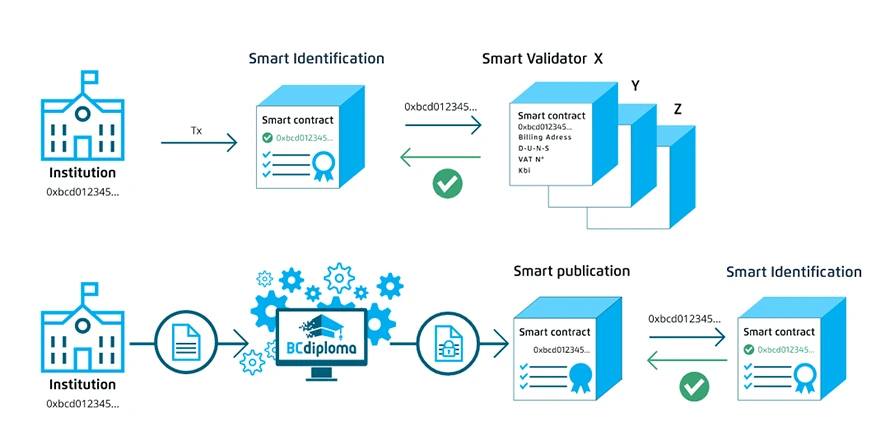
In the Cloud: the web part of the application, including the cryptographic algorithm enabling encryption, is deployed in the Cloud. The algorithm allows to answer question 2.) How is the GDPR complied with? In this regard, the Legal Opinion from the law firm Alain Bensoussan confirms the adequacy of the original process of BCdiploma (use of a persistence key allowing to permanently “cut off” access) and its compliance with the constraints of the GDPR.
Appendix 5 – Cryptographic algorithm
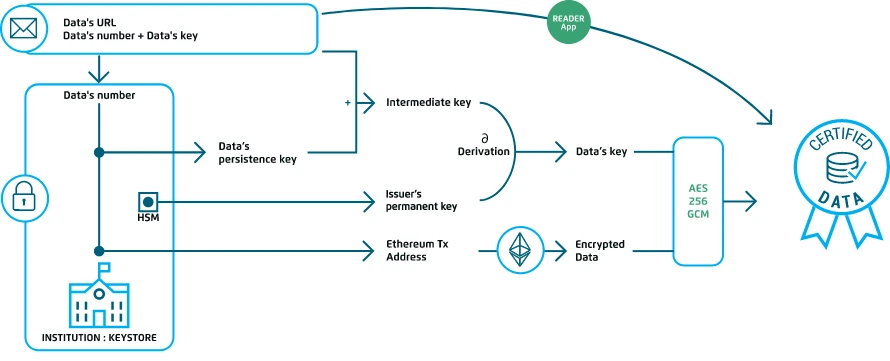
In addition, the “Reader App” component allows one-click access to certificates and their proofs, thus answering the question 3.) How is it possible to view a certificate immediately, i.e. without complex or centralized validation?
In this regard, the details of the evidence accessible from the certificate are described here – https://www.bcdiploma.com/proofs:
Appendix 6 – Proof of authenticity accessible from a BCdiploma certificate
In addition, key registries (including HSM) offering secure management of the 3 cryptographic keys allow access to the certificate and its “deletion” (in the sense of “permanent impossibility to decrypt the information”).
Understand numerical information with 3 examples
Example 1: Open badges to certify informal learning or achievement
What is an open badge and what are they used for?
Open badges were created in the United States in 2011 by the Mozilla and MacArthur foundations as a solution to recognize informal learning, i.e. skills acquired outside the traditional educational system. They can be awarded by any academic institution, online course provider, or by the organizers of events and conferences in the form of a unique digital certificate.
Open Badge is an e-badge digital standard that contains the following information:
- The issuer’s name;
- The recipient’s name;
- Award criteria;
- Issue date;
- Evidence of its earning.
By reading the information contained in the e-badge via a QR code or a URL link, one can verify and certify the skills acquired, and identify its holder. An e-badge can also take the form of a digital image containing this same metadata.
Open badges are typically stored in badge bags such as:
- Open Badge Passport;
- Badgr (formerly Mozilla Backpack).

They can be displayed and shared on social media to highlight specific commitments or technical skills and stand out to recruiters.
Examples of open badges

Open badges are mostly earned outside or alongside the traditional school system.
Indeed, open badges can be awarded for:
- Participating in an event;
- Completing an individual or group project;
- Attesting to specific commitments such as the eco-citizen badge;
- Valuing skills (e.g.: mastery of the Python coding language);
- Certifying the completion of MOOCs on Coursera for instance.
Example 2: Micro-certification for the delivery of blocks of competences
A micro-certification is “a certification attesting to the learning outcomes of a short course or module, and assessed in a transparent manner”.
Micro credentials allow for flexible, modular learning and can be used throughout one’s professional career. They can take the form of digital certifications such as open badges.
Why are micro-certifications suitable for attesting to a specific skill, or “block of competences”?
The 2018 French vocational training reform “Act for the freedom to choose one’s future” requires digital diplomas and professional certifications to be broken down into blocks of competences.
According to the French Labor Code, blocks of competences are “homogeneous and coherent sets of skills contributing to autonomous pursuit of a profession that can be assessed and validated.”
Approved training organizations can deliver digital micro-certifications to attest to the mastery of all blocks of competences that make up a course.
Micro-certifications allow students to assert their professional skills throughout their lives: learners can show these micro-certifications during their first job interview, for their professional development within the company, and throughout their professional career. Indeed, micro-credentials are designed to promote flexibility and mobility in the business world.
Example 3: Digital diplomas
What is the purpose of digital diplomas?
Digital diplomas are dematerialized and therefore more convenient for students: they can’t be lost and are very easy to share.
Furthermore, digital diplomas are much more advantageous for organizations because they allow them to:
- optimize administrative processes;
- easily store documents or data related to these documents;
- rapidly access information, especially upon requests from companies or students;
- demonstrate the school’s innovative approach;
- strengthen the bond between alumni and the university;
- fight against diploma falsification, which can damage the organization’s reputation.
The example of the University of Lille: read the White Paper
As demonstrated by the University of Lille project, a digital transformation project within a university can:
- Offer 100% digital, multilingual, tamper-proof diploma certificates to students, which are recognized worldwide
- Automate the process of producing and verifying credentials, increasing their reliability, and reducing their costs
- By providing employers with tamper-proof documents, they can have confidence in institutions and the documents they issue
Download the 2023 version of the White Paper
The example of emlyon business school

Based in Lyon, Emlyon Business School was the first business school to deliver digital diplomas to its students and alumni, i.e. over 18,000 people.
Since 2019, Emlyon Business School’s diplomas and certifications are automatically delivered and micro-certified on the block-chain in collaboration with BCdiploma.
Using a unique URL link, students can access their digital diploma containing all the necessary information to show their credential to recruiters and companies, and even post on social media.
Emlyon Business School’s diplomas can be displayed in several languages, and instantly verified or downloaded. This innovative service now boosts the school’s attractiveness and appreciation among students!
Visit emlyon’s website to learn more about the business school’s blockchain initiative.
Why opt for BCdiploma’s 100% blockchain digital credentials?
BCdiploma has created the very first digital credentials services based on blockchain data storage.
What are the benefits of blockchain digital credentials?
Digital credentials delivered on blockchain via BCdiploma are 100% secure, tamper-proof, verifiable and permanent.
Blockchain is a decentralized database and by nature a forgery-proof digital technology. Digital credentials are stored securely, making the falsification of information impossible. It therefore provides a guarantee of trust and security that allows students and learners to prove the authenticity of their achievements throughout their professional lives.
BCdiploma is specialized in micro credentials and digital certificates for diplomas, and allows any training organization to create its own e-badges using a turnkey platform.
Today, 170+ institutions in 21 countries trust BCdiploma to deliver their digital credentials. Discover Digital Credentials Successful Project Testimonial, by University of Lille.
Digital Credentials: state of play
Predictions: the future for digital credentials solutions
The International Council for Open and Distance Education (ICDE) has over 190 institutional members from over 70 countries, speaking over 40 languages, impacting over 15 million students across 6 continents.
Here is the analysis of the ICDE Working Group Report on the Present and Future of A. Digital Credentials (ADCs):
“ICDE institutional members will be profoundly influenced by the shift in importance from traditional forms of learning attestation to the new forms embodied by Digital Credentials. First, the demonstration of acquired skills and knowledge will be more important than where or how the learning occurred. Second, students will be the owners of their Digital Credentials and will have control over dissemination. Currently, institutions control the dissemination of academic transcripts and effectively limit public access through transcript fees and restrictions on the student data they are allowed to release. The advent of secure, un-hackable blockchain authentication processes will make Digital Credentials as, or even more secure, than traditional transcripts.”
The ICDE Working Group Report on the Present and Future of A. Digital Credentials (ADCs) predicts that block-chain will:
- Disrupt the market in student information systems
- Become the standard underlying technology for the issue of digital credentials
- Accelerate the end of paper-based cert-systems
International initiatives concerning digital credentials
The matter of blockchain digital credentials is addressed by many stakeholders:
European Commission – European Blockchain Partnership: the EBSI, which has a budget of €4M, has dedicated one of its four application cases to the issue of digital credentials. “Giving back control to citizens when managing their education credentials; significantly reducing verification costs and improving authenticity trust”. Since June 2022, EBSI has published on its website full documentation on the topic of these types of credential:
- Verifiable Credentials Explained (Chapter 1)
- Verifiable Credentials in Action (Chapter 2)
- Decentralized Identifier (DID) Methods (Chapter 3)
- Digital Identities (Chapter 4)
- Issuers Trust Model (Chapter 5)
- Open ID Connect for VCs (Chapter 6)
- Wallet (coming soon)

- Digital Credentials Consortium, a consortium of universities including MIT and Harvard University, is conducting open-source work towards a standardized ecosystem. “Our mission is to create a trusted, distributed, and shared infrastructure that will become the standard for issuing, storing, displaying, and verifying academic credentials, digitally.” (DCC white paper).
- In the private sector, BCdiploma, a French company established in 2017, is the blockcert ecosystem with the largest number of institutions: nearly 120, across 4 continents. BCdiploma has patented a method that combines cryptography and the block-chain, and markets a turnkey solution enabling any institution to issue latest-generation digital credentials. For example, ETS Global, the provider of the TOEIC® English test, has chosen BCdiploma blockcert technologies to certify and dematerialize the TOEIC® Score Report. On May 4, 2022, BCdiploma successfully renewed its 1EdTech – IMS Global Open Badges v2 certification.
Digital Credentials: standardization
The mission of the Verifiable Credentials Working Group (VCWG, W3C) is to facilitate and secure the expression and exchange of third-party verified credentials on the Web. This specification provides a mechanism for expressing such credentials on the Web in a way that is cryptographically secure, privacy compliant, and machine-verifiable.
The data model for verifiable credentials is a World Wide Web Consortium Recommendation, “Verifiable Credentials Data Model 1.0 – Expressing verifiable information on the Web” published on November 19, 2019.
Now in beta phase, these standards are being implemented by the Digital Credentials Consortium, EBSI and BCdiploma.
In parallel, the W3C is making progress on the decentralized identity specifications necessary for the implementation of Verifiable Credentials. June 30, 2022 marks an important milestone, with the publication of a decision reinforcing the place of DIDs.
What are the challenges faced while implementing Digital Credentials Solutions?
We can select four major challenges related to the adoption of dematerialization of diplomas and blockchain digital credentials: for each, the research work of BCdiploma will be presented.
“On chain” or “off chain” storage?
We see this injunction in a lot of invitations to tender: “no storage of personal information on chain”.
BCdiploma’s approach allows us to think differently about the problem at hand. We observe that the difficulties of scaling up and the difficulties of designing and creating a standardized ecosystem of digital credentials are increasing. Whether we are talking about the Digital Credential Consortium, Blockcerts or EBSI, there are many questions to answer: How should credentials be stored? In each holder’s wallet? In secure data stores or vaults? etc.
For BCdiploma, this issue is key and must be addressed first. So, our first R&D subject, now patented, was: “How to store, secure and authenticate data from a digital credentials register in a decentralized environment and then access it in one click – all in compliance with the GDPR?”
To sum up: we store the encrypted information directly on a perennial and secure register. This storage is carried out once and for all, allowing issuers to manage this information over the long-term. We use symmetrical cryptography (AES 256 GCM) to manage all issues relating to access to this information and its confidentiality.
We promote technologies that are not dependent on certain models, but are capable of adapting to expected changes in standards and output formats for digital credentials.
The main innovation of BCdiploma is that the output format (compatible with the W3C VC on-line verifier, the Open Badges on-line verifier, the EBSI standard, etc.) is a feature that can be developed on demand, from certified raw data.
Legal & Data privacy and security
EU’s General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) and California’s Consumer Privacy Act of 2018 (CCPA) may impose limitations on how personal data is transacted on the blockchain.

We invite you to read the complete research note published by jurist Aurélie Bayle: “Digital Credentials: legal proof and data privacy”.
The right to be forgotten is not the only issue of the GDPR that is met, but it is instinctively one of the first questions that arise when it comes to the block-chain. The compliance demonstrated by BCdiploma is a guarantee of credibility and responsibility towards its clients and partners.
Scalability and energy consumption
The relatively slow speed of block transactions may impose bottlenecks when it comes to scaling block-chain-in-education solutions worldwide. The issue of energy consumption is also a key point to monitor in order to develop technologies on a large scale.
BCdiploma handles this challenge in an extremely advanced way, being the first “multi-blockchain” application to:
- Respond to institutional projects that wish to work on their own consortium block-chain, for ecological issues among others.
- Be able to optimize writing costs by arbitration between different public block-chains, and thus offer an unequaled level of durability to these users. By the end of 2021, the block-chains supported in production were Avalanche, Smart Chain, and Ethereum. As soon as Ethereum 2 goes live, all BCdiploma applications will work only with proof-of-stake block-chains. Based on the most recent work, we estimate that after the launch of Ethereum 2, Ethereum’s energy usage will decrease by 99.95%.
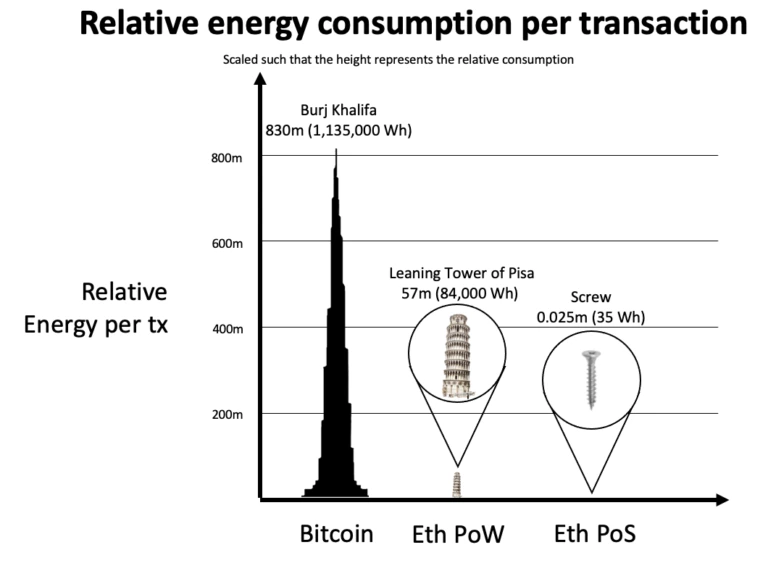
source: https://blog.ethereum.org/2021/05/18/country-power-no-more/
Indeed, the relevant technologies are rapidly evolving, and the stability of an e-cert ecosystem depends on its ability to keep pace with changes without jeopardizing already published information and framework components.
Market adoption and UX design
Lack of knowledge on how to harness the potential of block-chain-in-education solutions may lead to a slow market adoption of such innovations. However, the key point should be the ease of use of block-chain applications.
To address this point, BCdiploma has built a product with a “data centric” & “user centric” approach. We are freeing ourselves from the mere management of encryption hashes, which leads to a centralization or complexification of verification procedures. This makes our solution particularly innovative compared to other block-chain applications on the market.
The BCdiploma tool is very easy to use and to interface with management tools (it is compatyible with all data models), and each BCdiploma digital credential is:
- a nice “web object” designed by the issuer
- accessible in a single click
- verified by a simple on-chain consultation of proofs of authenticity
A video presenting our digital credentials user journey
Here is a detailed testimonial from a graduate who received his degree as a digital credential in 2023:
Conclusion
In the face of any technological revolution, the key question is: does it benefit all parties and user communities? Does this lead to a dependency on third-party actors or a centralization of data that can be exploited for other purposes?
The great value of block-chain digital credentials lies in the answers to these questions.
For the first time, digital credentials can be freely presented by their holders without the need for external verification. Considering that the background checking market is worth more than 3 billion dollars, it’s a breakthrough!
The benefits of digital credentials for higher-education institutions are numerous, including the end of fake diplomas, and the end of requests for duplicates and provisional certificates. Not to mention the immediate benefits in the administrative process of issuing and sending credentials.
Finally (and most importantly), the credential remains the property of each certificate holder: no centralization or exploitation by a third-party is possible. Combined with unequaled durability (with information is issued and secured for a very long period of time), we are definitely witnessing a major change in the way we work with certifying information.
FAQ
How do digital credentials work?
Digital credentials are digital versions of traditional qualifications such as a university or college degree. However, any company or training organization can create and issue credentials – in the form of badges for instance – to recognize a specific achievement, learning or skill.
How can Digital credentials support higher education?
Universities and colleges can use digital credentials to meet the expectations of younger generations of learners. Indeed, a university can issue a digital credential to a learner for completing a module in an online course, for instance. The learner can then add their certificate to their email signature, LinkedIn profile, and even personal website.
How do I add digital credentials to my resume?
Choose the e-badge you want to add to your Curriculum Vitae, download the image and add it to your Education section. Add a description sentence or two to list the enrollment and completion date, the name of the cert-issuing body, etc.
Links
Feedback from a university with over 80k students: discover the White Paper
Meet the BCdiploma team
To discuss your projects with our experts, schedule a meeting!
About the author

Luc Jarry-Lacombe, founder and CEO of BCdiploma, is an expert in blockchain and its applications in education and the public sector. With Vincent Langard, Luc wrote the international patent “Systems and computer-based methods of document certification and publication”. Luc is a regular speaker on blockchain and new digital identity standards.
[faq_1[What are digital credentials? | Digital credentials are secure, versatile, and verifiable online representations of qualifications such as diplomas, skills, transcripts, or certificates, enriched with metadata like issuer, criteria, evidence, and issue date.]] [faq_2[What are the key components of a digital credential? | They include the issuer (institution), the recipient, descriptive metadata (title, competencies, dates), and a built-in verification mechanism ensuring authenticity and portability.]] [faq_3[How are digital credentials created and issued? | Issuing bodies define learning objectives and assessment criteria, then use specialized platforms to automate issuance so recipients instantly receive their credential and can add it to a digital wallet.]] [faq_4[What types of digital credentials exist? | Types include digital badges (micro-credentials following Open Badges standards), digital certificates (for diplomas or professional credentials), blockchain-based credentials (immutable and verifiable), and stacked credentials combining modular achievements.]] [faq_5[What benefits do digital credentials bring? | For learners: portability, easy sharing, and career visibility. For institutions: efficiency, fraud prevention, and stronger branding. For employers: instant verification and clearer insights into applicants’ skills.]] [title[What are digital credentials? Definition, benefits and examples]] [description[Find out more about digital credentials, their benefits, examples, and the underlying technologies involved, including blockchain, Web 3 and open standards.]]