Blockchain plays a fundamental role in information verification. What is blockchain? It is a digital technology that allows secure and transparent storage and transmission of information. Every piece of data entered on the decentralized blockchain register can be viewed by all users of the network. Although the blockchain is currently used mainly as a trusted third party to verify the accuracy of transactions made with cryptocurrencies such as bitcoin, it is an important innovation for many business sectors including insurance, law, utilities and connected objects. Any information stored on the blockchain can’t be altered later on, which makes it an excellent solution to be used as an incorruptible record of digital credentials.
Why use blockchain for data transfers? Blockchain is an excellent way to ensure transaction security as it can be used to verify information and secure the data stored in the ledger: it is verifiable, secure and forgery-proof.
To better understand this process, let’s take a closer look at the 3 steps of information verification through blockchain, using the example of verifying digital diplomas and micro credentials.
Block chaining and hash verification
The blockchain is a chain of blocks. Each block contains the information entered in the register as well as its hash, bitcoin transactions details for instance. The hash is a line of code, unique to each block that represents its fingerprint or signature. It is generated when the block is created, and modified when a change occurs.
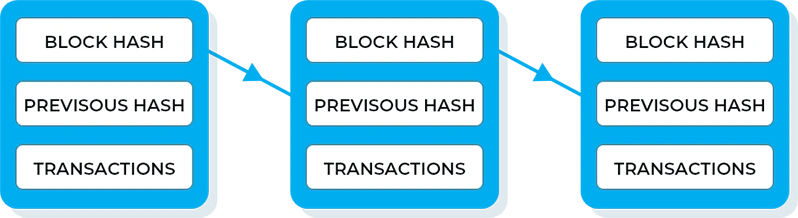
Every time information is added (with each new transaction):
- A new block is created containing the new information and its hash;
- This new block is “chained” to the previous one: it also contains the previous block’s hash;
- This way each block depends on the previous one.
For any attempt to modify the data of a block:
- The hash is also modified;
- ince each block is linked to the previous block through the hash, the modification will be detectable throughout the blockchain;
- All blocks become invalid.
Example of digital diplomas stored on the blockchain:
Blocks contain information about the diploma: school issuing the digital certificate, proof of validity, diploma data and timestamp.
If the student wants to hack heir digital diploma:
- Changing a single piece of data will cause the hash to change;
- All subsequent blocks become invalid;
- The fraud is immediately detected: complete failure for the hacker.
Verification of information by proof of work
Using powerful computers, it is theoretically possible to modify the data in one block and recalculate the hash of all subsequent blocks so that the fraud can’t be detected.
To counter this, the verification of information by the blockchain relies on a second mechanism: proof of work by “miners”.
Indeed, each time a block is added:
- Some blockchain users, called “miners”, have to solve a complex mathematical problem requiring great computing power;
- Just like an equation, the mathematical problem is very complex and time-consuming to solve, but its validity is easy to verify;

- Only once the problem is solved can a new block be added to the chain.
This proof of work process prevents hackers from modifying a block or its hash.
So in our example, a student with hacking skills and a high-powered computer still would not be able to modify their degree without the blockchain certification mechanisms detecting the fraud. This is the second layer of security of blockchain technology.
Verification by all users of the network
Finally, there is a third mechanism to ensure reliability of the data contained in the blocks of the blockchain.
When a new block is added to the chain, it is sent to a network of computers. Then it is submitted for validation by each node, and added to all copies of the database. This network of nodes help harmonize the authenticity of the blockchain certification.
A blockchain network is said to be decentralized and distributed: all members have access to exact copies of the data ledger. Each member of the network can check the validity of the information contained in the new blocks with their copy of the register.
It then operates according to consensus:
- Each member checks the information in the new block;
- If the information is correct, the user adds this block to their copy of the chain;
- The copy held by the majority of users is the one considered valid.
Then, the new block will become visible to other users. It can no longer be modified, which is a key security feature of the blockchain system.
The combination of these three mechanisms − hash, proof of work and network of nodes − make blockchain an incredibly secure and forgery-proof technology with high probative value when it comes to information verification, from bitcoin transactions to digital micro credentials.
Blockchain authentication : how can blockchain be used for the verification of a learning credential or diploma?
Blockchain authentication is revolutionizing the certification system for credentials : it allows organizations and universities to issue digital certificates and diplomas in a secure manner.
With blockchain and digital credentials, students receive a certified digital diploma in which all their educational information is stored. This verified credential may be very useful for job opportunities.
They can share this digital diploma on their CV, on their social media profiles, and even send it directly to recruiters. With blockchain certification, there is no need to verify information. Certificates based on blockchain are forgery-proof which is a huge improvement in the fight against CVs and diplomas fraud.
BCdiploma’s 100% blockchain diplomas: authentic and verifiable by nature
Are BCdiploma’s blockchain diplomas really forgery-proof?
By nature, BCdiploma’s diploma data is impossible to falsify. The blockchain’s inherent information verification feature ensures the integrity of the diploma information stored on the blockchain, granting the blockchain certificate evidential value.
When the issuer decides to use blockchain technology to issue digital credentials, BCdiploma makes an encrypted record of:
- The issuer’s name
- The recipient’s name
- The credential awarded
- The date of creation
These pieces of data are encrypted right onto the blockchain. This means that every blockchain credential is incredibly secure.
Any person, student, training organization or recruiter, can verify in real time the validity of the information stored on the blockchain diploma.
How can the diploma issuer’s identity be verified?
BCdiploma has developed a specific patented system to verify the identity of the diploma issuer.
It allows verification of the certificate by examining:
- Data published by the institution;
- All the blockchain evidence attesting to its authenticity.
The identity and legal existence of institutions issuing 100% blockchain BCdiploma diplomas are verified by “validators”. These validators collect formal evidence of the identity and credentials of the degree-issuing institutions. The evidence of this validation is also recorded on the blockchain, making it forgery-proof. Choosing blockchain for diplomas is a fantastic security guarantee!
FAQ about blockchain verification
How does blockchain verification work?
For added security, individuals can store their digital credentials on a blockchain. The verified document’s unique fingerprint is secured on a worldwide network of blockchain nodes. Blockchain data is 100% secure and tamper-proof, and its integrity and origin can be instantly verified. That’s why it is the cornerstone of bitcoin transactions for instance. And by using turnkey online solutions, no blockchain knowledge is needed to verify a document.
What are the main benefits of blockchain?
When a credential is issued and recorded on the blockchain, the record of the credential is written into the list of blockchain transactions. Because the blockchain is public, any network user can make sure the credential was recorded at the correct time, thus verifying the information and ensuring the security of the system as a whole.
How can blockchain be used for diploma and credentials verification?
Blockchain is revolutionizing the certification system for diplomas and credentials, as it allows organizations to issue digital certificates in a secure manner, with blockchain evidence attesting to their authenticity. In turn, any person, student or recruiter can verify in real time the validity of the information stored on the blockchain credential or diploma. The integrity of the credential information stored on the blockchain is guaranteed and forgery-proof.
[title[Blockchain for Information Verification: Secure & Transparent Tech]] [description[Blockchain plays a fundamental role in the process of information verification. How does it work ? BCdiploma answers all your questions.]]