Digital certificates have become indispensable in the digital realm, vital for securing online interactions, verifying identities, and safeguarding data.
What exactly is a digital certificate?
It’s an electronic verification tool for confirming the identity of a person or entity, or the legitimacy of a digital document. These certificates are crucial for secure communication, authenticating parties in transactions, and ensuring data integrity. Their application transcends IT security, reaching into healthcare for professional identity verification and data protection, finance for secure transactions and client identification, and education for validating and protecting academic records, making them crucial in any setting requiring secure digital authentication.
Digital certificates VS Broader credentials
The nuance between digital certificates and broader credentials is subtle yet significant. Digital certificates are specialized digital credentials designed for secure online communications and data transfer, equipped with keys and signatures to safeguard document access and prevent unethical data breaches. Organizations and institutions issue these certificates to recognize the integrity and dedication of individuals completing courses or programs, including details like the recipient’s name, award criteria, skills, knowledge, and document validity.
Types of Digital Certificates
Digital Certificates include:
- SSL/TLS Certificates for website-user browser communication security.
- Electronic Signature Certificates for authenticating digital document signatures.
- Public Key Certificates in public key cryptography.
- Server Certificates for authenticating web servers to clients.
- Client Certificates for securing individual or device access to online services.
- Root Certificates from trusted authorities, establishing trust chains.
- Email Certificates for email security.
- IoT Certificates for connected device authentication.
The focus here is on digital document attestations, particularly in academia and training.
Termed digital credentials, they cover micro-credentialing, digital badges, and all academic certificates suitable for resumes. All are concrete examples of Digital Certificates, used by institutions to offer a modern service to their learners, in line with job boards and the expectations of recruiters.
Digital Certificates’ Importance in Academia and Profession

Showcasing credentials to employers
In competitive fields, showcasing credentials in resumes is essential. Employers use these for quick assessment of a candidate’s suitability. In sectors demanding specific skills or advanced training, these credentials can be the differentiator. More than just proof of skill, they signify commitment to ongoing professional development. A well-crafted resume with relevant degrees significantly boosts interview prospects.
Originally paper-based, these certificates have evolved in the digital age to be more accessible, shareable, and verifiable online, increasingly important in higher education for authenticity and reputation. Many standards have emerged to make these digital certificates interoperable: we can mention Open Badges, whose latest version 3 is compatible with the W3C’s Verifiable Credentials standard, and also standards from the 1EdTech Consortium such as LTI.
Digital Certificates in Resumes
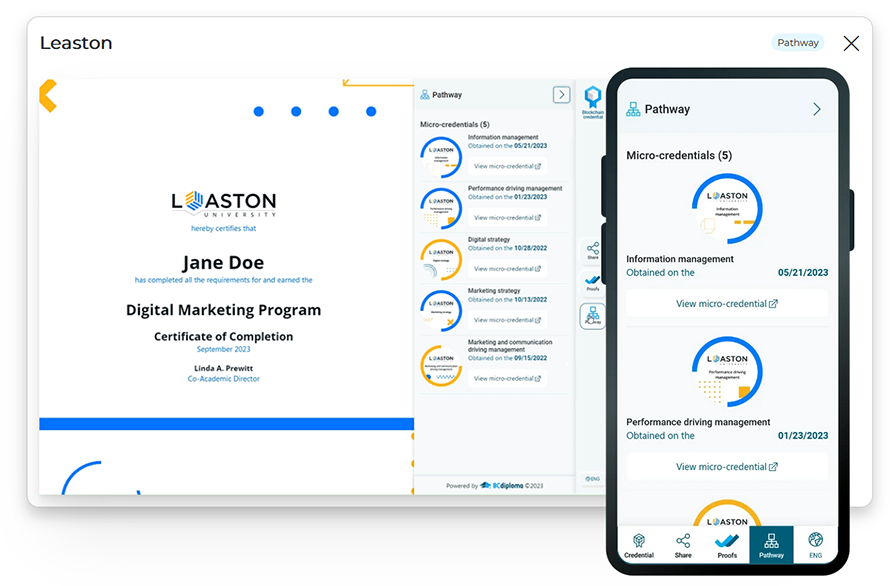
Typically, digital certificates in resumes include:
- Academic Certificates from educational institutions.
- Professional Certifications from recognized bodies.
- Skill-Based Certificates for specific abilities.
- Competence Certificates from professional bodies.
- Participation Certificates for events.
For example, Stanford Online offers a range of digital certificates from participation statements to professional certificates and academic credits:
Statement of Participation
Issued for offerings that require less than 20 hours of coursework and do not require assessment.
Record of Completion
Issued when a single course has been followed and successfully completed, often accessible as a badge.
Certificate of Completion
Issued for a single course followed and successfully completed in a program requiring more than 20 hours of attendance, often in the form of a detailed certificate.
Certificate of Achievement
Issued when a program of 36 to 150 hours has been fully attended and completed, includes learning outcomes assessments.
Professional Certificate
Issued for a program of more than 150 hours, with rigorous assessment of content mastery and proficiency.
Academic Credit and Degree Courses
For academic credit-bearing courses and programs, the Digital Certificate is a university credit, affirmed in an official university transcript.
University Degree
The pinnacle, for a complete degree, such as a Master! It can be accompanied by a transcript or a Learning Pathway detailing all courses obtained during the program.
This credentialing framework and its implementation using blockchain technology was awarded a Gold Award at the 1EdTech Learning Impact Conference, in the Digital Credentials category.
Technologies Behind Digital Certificates
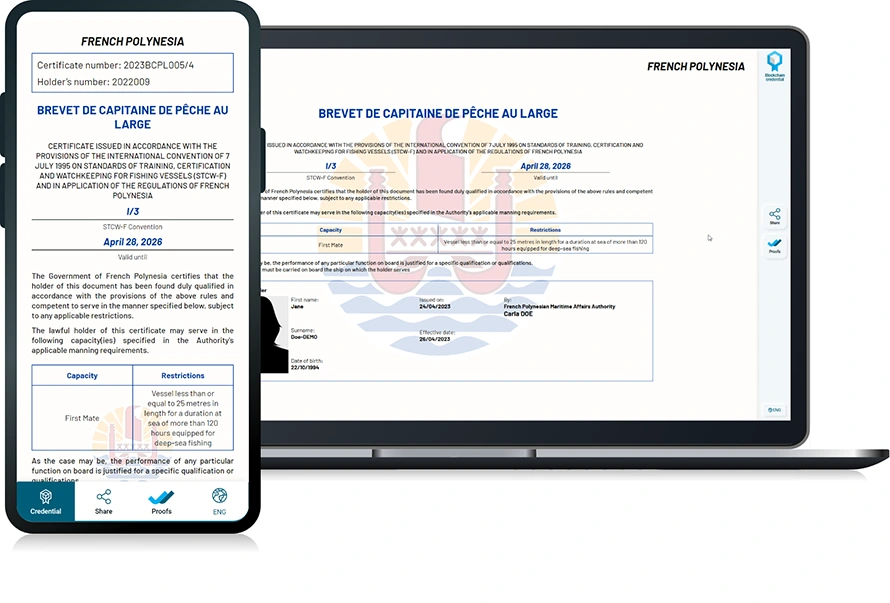
Technologies involved include centralized systems, blockchain technologies for lifelong validity, and emerging Web3 & Self Sovereign Identity Technologies. These technologies enhance verification and offer new capabilities.
Centralized Technologies
Many credentialing platforms rely on classic centralized technologies, sometimes secured using digital vaults or blockchain anchors.
Blockchain Technologies
Some publishers, like BCdiploma, leverage blockchain properties to offer lifetime valid Digital Certificates with real-time data read from a blockchain.
Web3 & Self Sovereign Identity Technologies
The emergence of decentralized identifiers (DIDs), web3, NFTs, and Soulbound Tokens has brought a new dimension to the verification of digital certificates. These technologies are also used in large-scale institutional projects, such as EBSI in Europe or the Digital Credentials Consortium. In both these examples, the standard used is called Verifiable Credentials. It is a standard enacted by the W3C. Some platforms are already offering turnkey services for Web3 Digital Certificates, providing learners with wallets. An introduction to the concept of Web3 Digital Certificates is available here. You will find complete answers to the questions:
- What is a Web3 Digital Credential?
- Why should you be interested in Web3 Digital Credentials in the academic world, for diplomas or professional certificates, for example?
- How to design a Web3 Digital Credential? How does a learner receive and use a Web3 Digital Credential?
Challenges in Verifying Digital Certificates
Combat global diploma fraud
Academic certificate verification is crucial to combat global diploma fraud. Digital certificates can use high-level encryption and blockchain recording for secure and tamper-proof records, surpassing traditional methods. Traditional paper versions of certificates generated significant costs and tedious verification processes. Even today, on many fraudulent websites, one can buy relatively well-made fake diplomas… a nightmare for prestigious universities and recruiters.
Recent credentialing platforms allow instant verification, improving efficiency and data privacy compliance, and have established themselves as top-tier partners for educational institutions worldwide as well as for businesses and recruiters.
Examples and Impact of Digital Certificates
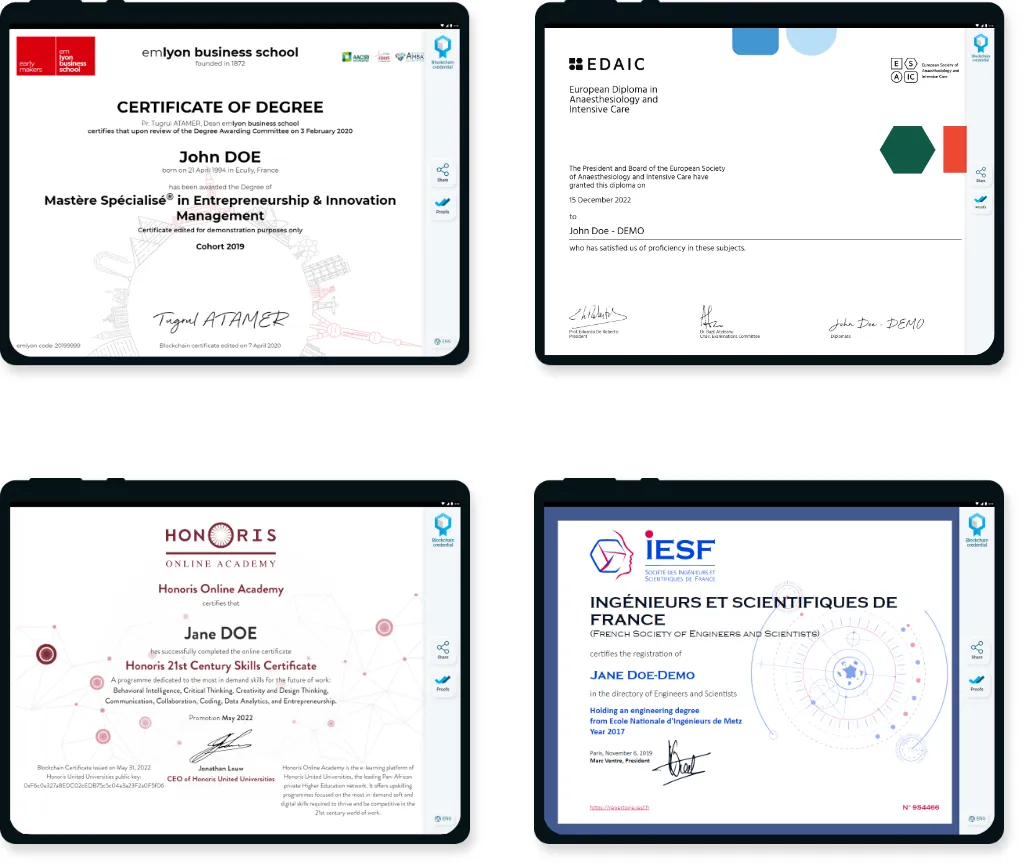
A cutting-edge approach
Digital Certificates offered by BCdiploma represent a cutting-edge approach to certifying all types of academic and professional achievements. The technology is based on advanced use of blockchain, ensuring the authenticity and easy verification of documents. They are stored in a tamper-proof format without a time limit.
White Labeling
Additionally, BCdiploma implements a unique concept of White Labeling: attestations can be custom designed in a full-page web format and are directly viewable on the issuing institution’s website, eliminating the need for a third-party verification platform. Thus, Digital Certificates are directly accessible in the institution’s environment.
Our Portfolio of Digital Certificates
Below, you will find a range of examples of Digital Certificates, for various uses: Custom Certificates, micro-credentials, proof of attending, Admin certificates, Learning Pathway…
Digital certificates have revolutionized recognition and certification, offering secure, verifiable proof of individual achievements, transcending traditional paper credentials. They enhance transparency, reduce fraud, and allow efficient qualification verification, crucial for informed decision-making in various sectors.
[title[Exploring Digital Certificates: Types, Impact, Academic Insights]] [description[Explore digital certificates’ role in securing online data, especially in academia. Discover their impact on authentication and data integrity.]]